Behavioral Segmentation Definition with 8 Examples & Strategies
Behavioral market segmentation is an effective way to study and categorize the target audience to provide more personalized experiences and offers. According to the survey, 96% of marketers say personalization drives repeat purchases, and 94% say it helps increase sales. The cornerstone of personalized communications with consumers is a deep understanding of how to group them using psychographic and behavior-based segmentation methods.
In this article, we will explain what behavioral segmentation is, consider its types, and explore examples and data enrichment tools to help you understand how it can improve your marketing strategy and sales growth.
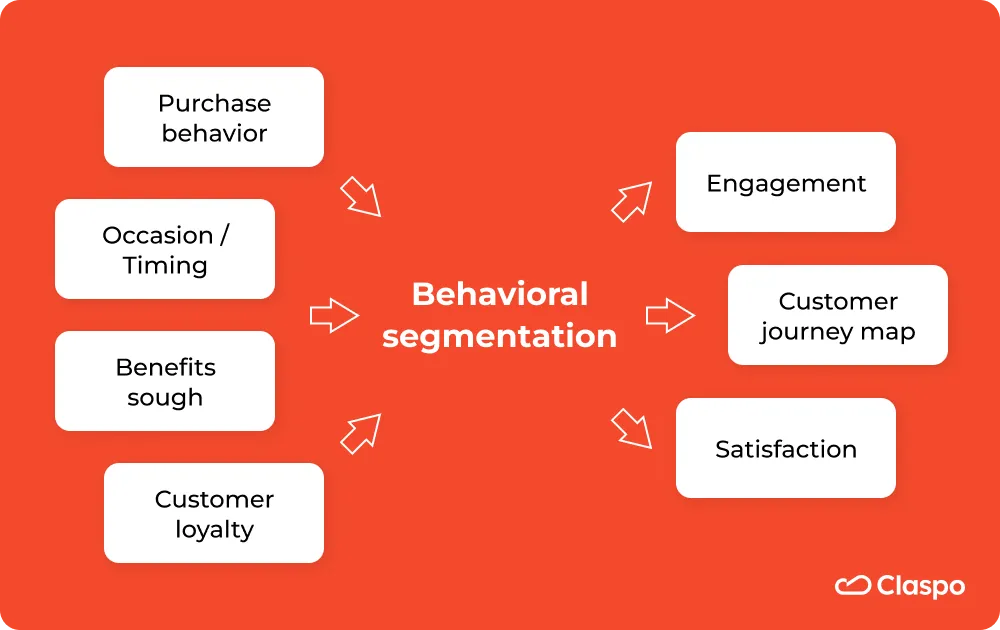
What is behavioral segmentation?
This segmentation focuses on buyers' attitudes, purchase decisions, and activities, such as spending habits, usage frequency, loyalty, and other behavioral characteristics. Through behavioral segmentation, marketers can better understand their target market and tailor their strategies to meet their needs.
The most common criteria for behavioral segmentation include:
- place and frequency of purchase;
- frequency of product consumption;
- consumer benefits (such as service, quality, speed, etc.);
- attitude towards the product and expectations;
- reason for purchase;
- level of involvement.
It's interesting to note that these parameters are highly correlated. According to a study, more than 50% of consumers want brands to use preferences, favorite products and categories, and purchase history as personalization elements.
However, these parameters are not exhaustive. You can tailor them to suit your business needs and incorporate additional behavioral market segmentation criteria.
For example, in email marketing, you can analyze subscribers' behavior based on their activity level (actively reading emails, occasional reading, not reading at all) and adjust the marketing strategy accordingly to enhance database efficiency.
One more classic example is RFM segmentation, where subscribers are grouped based on three criteria:
- R (Recency) – time since last purchase;
- F (Frequency) – order frequency;
- M (Monetary) – purchase amount.
For example, those who haven't made a purchase for a while could receive a compelling offer to re-engage them. If a customer has made several purchases but has since become inactive, it's important to investigate the reasons for this, which might involve service issues. In such cases, offering an additional discount may not be sufficient motivation for a new purchase. Conducting a survey among segment members can help clarify the situation.
Here are some examples of behavioral segmentation by industry:
- Clothing retailers: categorize customers by purchase frequency, such as frequent buyers, occasional buyers, and one-time buyers.
- Automobile companies: group customers by the benefits they value most, such as status seekers, value shoppers, environmentalists, etc.
- Fitness brands: categorize clients by the goal they are trying to achieve, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or general wellness.
- Food brands: organize audiences by dietary preferences, such as vegetarians or vegans, health-conscious, and so on.
- Financial services: segment clients based on their savings habits, such as regular savers, occasional savers, or long-term investors.
- Technology companies: categorize customers based on their adoption of new technologies, such as early adopters, mainstream adopters, and laggards.
8 Types of Behavioral Segmentation
Segmentation based on consumer behavior is characterized by the use of different variables tailored to the product or business itself. Each of these parameters provides valuable information that helps understand the behavioral patterns of specific consumer groups. Let's look at some of the most common types of this segmentation.
1. Buying Behavior Segmentation
This type categorizes customers by identifying their buying habits using purchasing history. It takes into account variables such as:
- frequency of purchases,
- types of products purchased,
- timing of purchases (e.g., impulse vs. planned purchases),
- average order value.
Customers could be grouped as first-time buyers, regular customers, or seasonal shoppers. By understanding purchase behavior, you can personalize each customer's journey. For example, greet newcomers with welcome offers or share educational content to help them get to know the brand. According to statistics, 86% of online shoppers are more likely to buy something from a company they don't know if they receive a discount. Take a look at how you can use Claspo's welcome pop-ups to encourage new visitors to make their first purchase on your website:

You can offer new users a free trial plan to encourage them to use the service. Trial-to-pay conversion rates vary across SaaS industries. CRM users achieve the highest rate, with a 29% conversion rate. However, the median conversion rate is 23%. By the way, we have nice widgets for this purpose as well. Take a look at one of them:

Offer various perks to loyalty program participants. According to a survey, among the loyalty drivers, consumers mentioned exclusive discounts on products or services, special access to specific items or events, and more.
Specifying criteria such as purchase frequency, average order value, and product categories when segmenting your audience will help you identify valuable customers and focus on retaining them. Statistics prove the importance of this type of behavioral segmentation: 32.3% of consumers will switch brands if communications do not match their current buying behavior.
2. Usage Behavior Segmentation
This type of segmentation categorizes customers based on their level of use or consumption of a product/service. Typically, it considers variables such as the frequency, volume, or intensity with which a product or service gets used. In this case, customers are classified as:
- heavy users (frequent and high-volume users),
- moderate users (regular but moderate-volume users),
- light users (infrequent or low-volume users).
With segmentation based on the level of consumption or usage, you can provide different customer groups with relevant offers. For example, heavy users will likely be interested in advanced features, access to beta programs, and exclusive products. Tell moderate users about the various features they use little or not at all. Explain how the tools work and how they will improve the customer's work/life. This will help keep them interested and encourage more usage and deeper engagement with your product. Light users may appreciate a variety of educational content.
3. Occasion-Based Behavioral Segmentation
With this type of behavioral segmentation, you categorize customers into groups based on the occasions that influence their purchase decisions. These occasions can be seasonal, holiday, or related to significant life events, such as birthdays or weddings. By segmenting your audience, you can identify interesting patterns in their buying behavior related to specific occasions or events. For example, you may notice a spike in sales of certain products or categories on the eve of major holidays or regular seasonal events, such as the start of school or vacation season.
Understanding when consumers are more likely to purchase specific products allows you to launch targeted marketing campaigns with themed promotions. Tailoring your messages and offers to the specific needs of your customers during certain events will help make them more relevant and drive sales.
Our webpage widgets are great tools for occasion-based marketing. You can use them to announce upcoming holiday sales, direct website visitors to pages with current offers, etc. For example, you can announce a big sale using a countdown template. This is a great way to get your visitors excited about the event. Collect their emails to remind them of the sale and send them a promo code.
4. Loyalty-Based Segmentation
With this approach, you group customers by their level of loyalty and commitment to the company or brand. This way, you can prioritize customer retention to increase their lifetime value. To determine the level of loyalty, you should track the following metrics:
- purchase history,
- repeat purchases,
- customer feedback,
- engagement indicators (social media interaction, website, and app visits).
Typically, loyal customers show consistent engagement and a positive attitude toward the brand. Working with various segments requires different incentives. For example, create loyalty programs with exclusive benefits for valuable customers to encourage repeat purchases. For customers considering changing brands, use personalized offers, discounts, and other perks to attract them back.
5. Benefits Sought Segmentation
With this type of customer behavioral segmentation, you divide your audience based on the specific benefits of your company or product or the value propositions prioritized by different groups of people. By understanding what drives customer decisions, you can tailor your marketing messages to meet the unique needs of each behavioral segment. For example, a message for price-conscious customers might emphasize discounts and value, while for consumers who care about product quality, it should emphasize premium materials and craftsmanship.
6. Customer Journey Stage Segmentation
Following this strategy, you group customers based on the stage of the customer journey they are currently in. Let us remind you what these stages are:
- awareness,
- consideration,
- decision,
- retention,
- advocacy.
By understanding where your customers are in the buying cycle, you can more accurately target them with content and offers that move them to conversion and the next step in the funnel.
Awareness Stage
Audience characteristics: users try to understand the problem they are dealing with. At this stage, they search for and read content related to it, such as various articles like “How to...” and “Top 10 reasons...,” etc.
What can you offer them: provide this audience with valuable insights into their problem, avoiding intrusive advertising. Be helpful by offering visitors relevant case studies, guides, checklists, and more.

Consideration Stage
Audience characteristics: these users have already gathered enough information about their task and are now evaluating solutions that can help them. They are focusing on your product’s advantages and characteristics.
What can you offer them: you can use widgets to draw these visitors' attention to free trials, reviews, success stories, product comparisons, and more.

While Claspo is working on implementing this template, use our slider to display text, photo, or video reviews on the website as a slideshow.
Decision Stage
Audience characteristics: visitors return to your site frequently to check prices, exam delivery terms and return policies, view the About Us page, and sometimes reach out to the support team. They also search for information related to your company using Google or other systems.
What can you offer them: encourage potential customers to make a purchase with discounts, promo codes, free shipping, or any other perks that resonate with your target audience and add value to the purchase.

Retention Stage
Audience characteristics: after the purchase, customers begin to use the product and form their opinion on whether they are satisfied.
What can you offer them: to bring these users back to the site for new purchases, offer them personalized product recommendations and invite them to participate in a loyalty program. Also, at this stage, you should collect customer feedback to address any potential issues in advance. Moreover, positive product reviews posted on the website will encourage other prospects to place orders.


Advocacy Stage
Audience characteristics: if you're lucky, or rather, if you've done everything right, your customers are satisfied with your products and service to the point where they recommend the company to others.
What can you offer them: develop the loyalty of such brand advocates by offering them to participate in a referral program. Pamper them with exclusive benefits for spreading their positive feedback.

7. Engagement Level Segmentation
This type of behavioral segmentation allows you to categorize consumers based on their level of interaction with the brand across different touchpoints, such as your social media pages, email campaigns, website, app, advertising, offline store, and so on. For example, by identifying customers with different levels of engagement, you can optimize the frequency of email campaigns. You can send 3-4 emails a week to highly engaged subscribers, while it's better to send only one email a week to low-engagement customers.
That way, your subscribers won't complain about spam, and you can save your budget by reducing the number of unopened emails you send.
8. Satisfaction Level Segmentation
This approach to behavioral segmentation groups customers according to their level of satisfaction with a brand or product. By identifying satisfied customers, you can encourage them to leave feedback, which is a critical factor in driving sales. According to statistics, 91% of consumers are likely to recommend a company to their family and friends after a positive customer experience. On the other hand, understanding the opinions of dissatisfied customers will help you identify and resolve problems, thereby minimizing customer churn. Claspo can gather that valuable feedback for you. Keep reading to learn about our cool survey widgets!
Why Should You Start Using Behavioral Segmentation?
The benefits of behavioral segmentation are the following.
- Personalization. Behavioral market segmentation becomes even more powerful when combined with generative AI personalization, making it possible to respond correctly to the client's actions. Forming a relevant offer for each segment that arrives at the right time and through the proper channels will more effectively lead the client through the sales funnel.
- Forecasting. Based on the data received from behavioral customer segmentation, you can make forecasts for future purchases and learn how to stir up interest to increase sales if necessary.
- Saving resources. Develop marketing campaigns that target the most relevant segment, avoiding unnecessary costs associated with communicating with inappropriate audiences.
- Efficiency. It is easier to evaluate the actions within each behavioral segment and adjust campaigns based on this.
- Performance. By analyzing behavioral market segmentation, you can see how well your business is doing overall. This means looking at whether brand loyalty and purchase frequency are increasing (and which segments) and whether the growth is positive or negative. This helps to understand if you’re meeting goals or need to rethink your strategy.
Behavioral Segmentation Examples
Structuring your customer base allows you to use effective marketing techniques to increase engagement, conversion, loyalty, service satisfaction, and sales. We will provide behavioral segmentation examples to demonstrate how they can be used and inspire you.
Purchasing Behavior Segmentation from Sephora
Let's look at Sephora's customer segmentation strategy by purchase frequency.
For frequent customers, the brand offers various benefits through its Beauty Insider loyalty program, including gifts and rewards. Participants in this behavioral segment also enjoy exclusive access to new products and invitations to special events.
When communicating with moderate customers, the company relies on emails containing personalized product recommendations and announcements of upcoming sales. They are also reminded of their accumulated loyalty points to encourage new purchases.
For occasional customers who make approximately one purchase every six months, the brand focuses on seasonal promotions and holiday gifts.

Occasion Purchasing with Oreo
The famous cookie brand actively uses occasion-based marketing in its strategy. It uses major holidays such as Christmas, various social occasions such as Pride Month, and even upcoming movie premieres as the basis for its campaigns. However, the brand does not ignore client holidays either. For example, subscribers receive an offer to customize an Oreo cookie for birthdays:
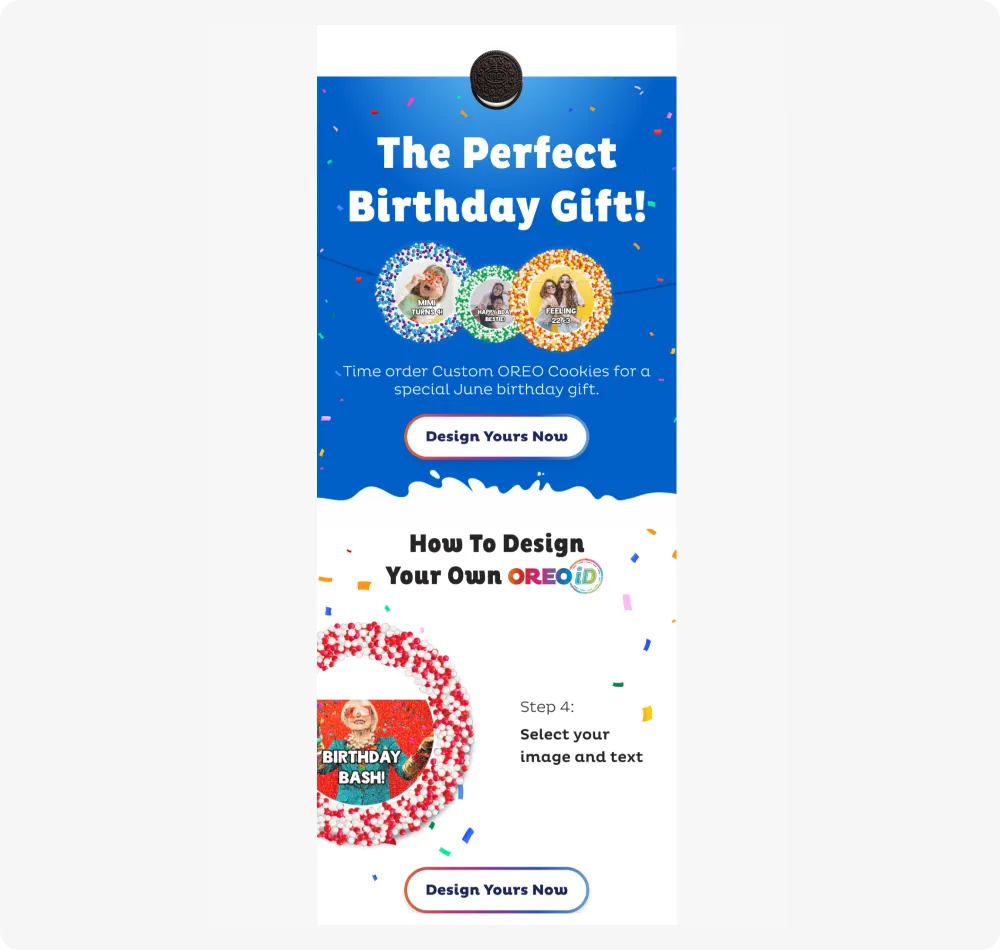
The company likely uses behavioral segmentation to create groups of recipients for these emails. When building a segment for an email like Oreo's, the following conditions are specified:
- The customer ordered a birthday cookie.
- The order was placed in June.
This method is useful when you don't have information about the customer's birthday but know that the person may be interested in a gift around a specific date. By the way, with Claspo pop-ups, you can easily collect birthday information directly from your customers to send personalized offers later.

Benefits Sought from Starbucks
Let's look at Starbucks' behavioral segmentation as an example of how the company communicates with its social media audience and the key messages it shares. Benefits-seeking research helped the brand's marketers identify the top reasons why customers choose its products. They tailored their communications to those reasons. Several of the brand's social media posts show how they appeal to the audience segment that values product quality the most.
These posts talk about the origin of the coffee beans, exclusive blends, and other quality-related topics. They also appeal to sustainability-conscious consumers, who are told how to consume wisely with Starbucks.

This way, different audience segments see the information that resonates with them the most. They begin to associate the brand with their values.
Customer Loyalty from Nike
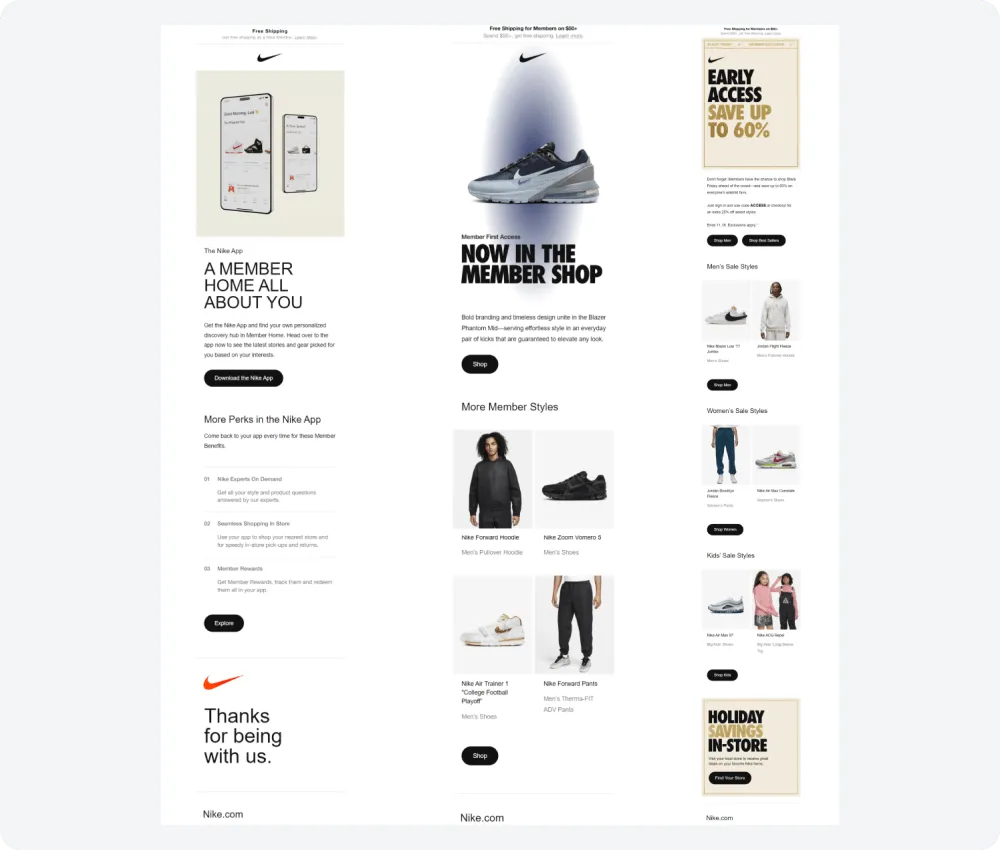
This well-known brand utilizes its own Nike Membership program to gather data for behavioral segmentation of its audience based on loyalty levels. Communication with new customers focuses on offering various enticing deals, introducing different products, and encouraging them to join the company's loyalty program.
Newcomers who join Nike Membership are informed about the benefits they can access. Regular program members receive exclusive offers, birthday rewards, and early access to major sales events like Black Friday. This customer segment also receives occasional emails with updates about the progress of the rewards program.
Interaction with the brand's ambassadors is taken to a higher level: they are offered exclusive discounts, free merchandise, and opportunities to participate in Nike-sponsored events.
Client Journey Stage Segmentation from Coca-Cola
Coca-Cola has an extensive strategy for customer journey stage segmentation. Significant budgets are invested in each stage. For example, to build brand awareness, the company does the following:
- engages in mass media advertising (by now, everybody probably knows the ‘Holidays are Coming’ jingle),
- sponsors major events (such as the FIFA World Cup)
- launches viral campaigns on social media.

At the consideration stage, the brand often partners with influencers who demonstrate the product to their followers. In the retention stage, loyal customers are offered special merchandise, collectibles, etc.
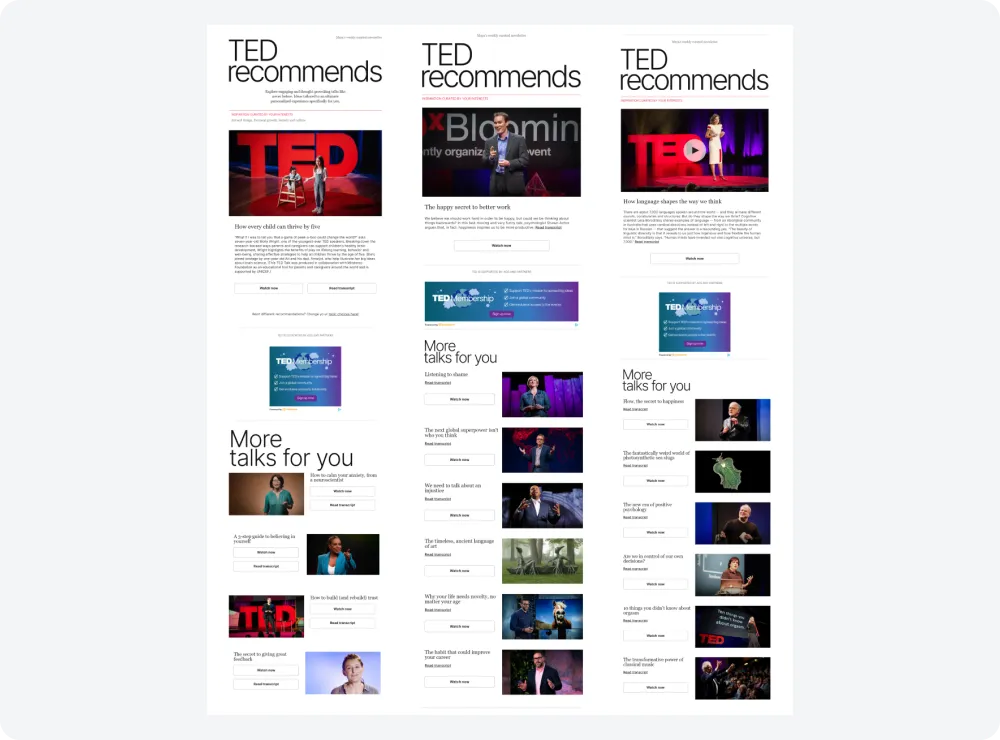
Usage Behavior Segmentation with TED
The TED platform, which is full of educational content and inspirational talks by various speakers, utilizes behavior segmentation to better understand what the target audience is interested in. To do this, they monitor metrics such as video views, likes, and shares, conduct surveys, and collect user feedback.
For example, a brand can divide its users into regular and occasional viewers. With this in mind, the company's marketers can choose an email frequency strategy. For content, the audience can be segmented into topic enthusiasts and general explorers. Based on this, the company can tailor the content of its emails. Topic enthusiasts will receive notifications when new content about their favorite subjects is published. For general explorers, a weekly playlist can be created based on each user's browsing history.
Engagement Segmentation from Fitbit
This behavioral segmentation is based on the frequency of logging into a personal account on a website, interaction with the brand on social media, etc. Fitbit can analyze consumer engagement levels based on their use of the brand's wearables and digital products, including activity tracking, various exercises, goal achievements, and participation in challenges. The more people utilize these features, the more engaged they become.
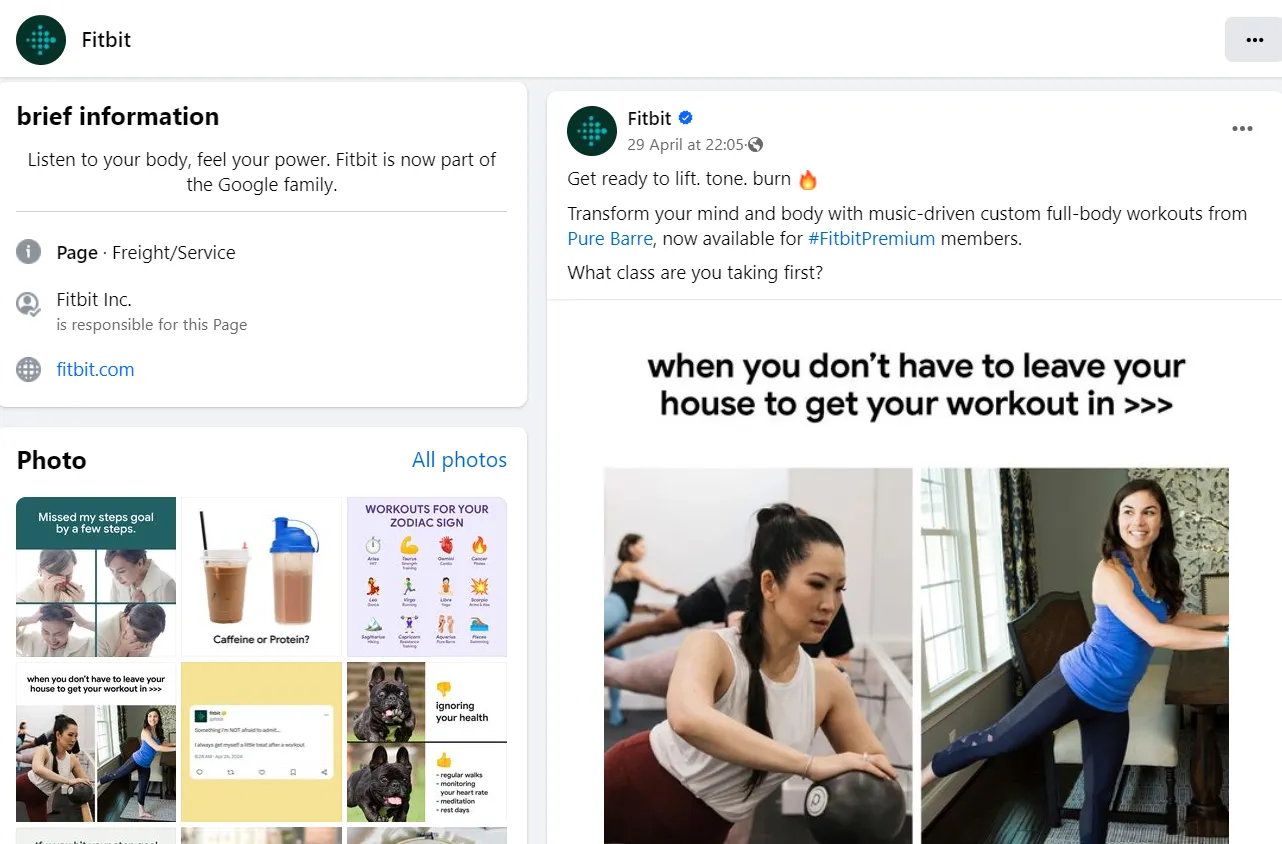
By segmenting the audience according to this principle, a company can, for example, pinpoint users most likely to subscribe to the Premium program and concentrate its marketing efforts on them. Additionally, the brand can identify potential advocates among the most engaged users and encourage them to create user-generated content.
Satisfaction Level Segmentation from Bolt
The transportation company Bolt, which offers taxi rides, among other services, employs various behavioral segmentation options. However, one of the brand's primary criteria is customer satisfaction. After each ride, app users are prompted to rate the service provided by the driver. This enables the company to monitor driver qualifications and gauge customer satisfaction levels. Additionally, Bolt occasionally conducts surveys among its newsletter subscribers.
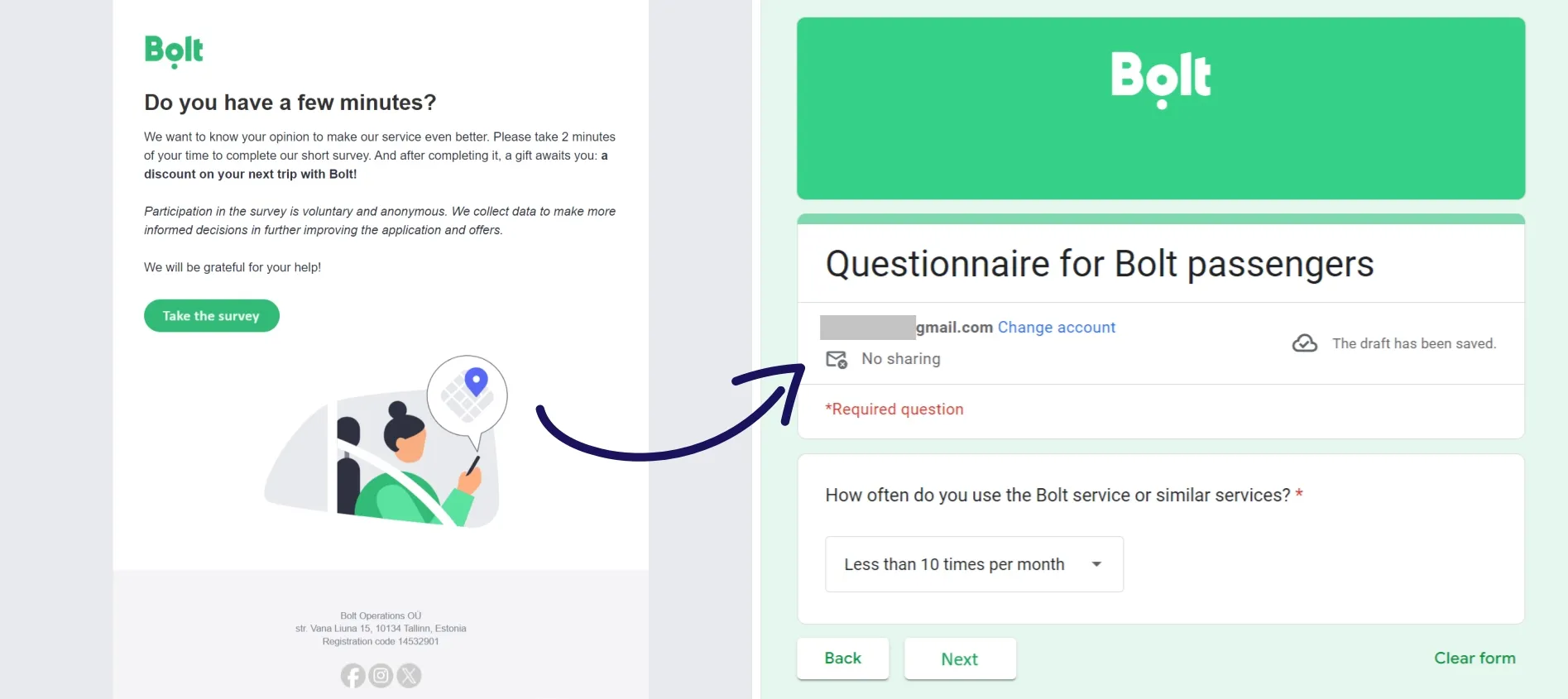
By segmenting the audience based on satisfaction levels, the company can personalize communication for different segments. For instance, loyal users receive additional promotions, such as invitations to install the Bolt Food app or utilize the scooter rental service. For less satisfied customers, the company communicates to improve its service and address their concerns.
Behavioral Segmentation Strategies: How to Implement in 6 Steps
Like any other form of audience grouping, behavioral segmentation is not a standalone concept. It's a component of a comprehensive strategy aimed at personalizing and enhancing the customer experience, ultimately leading to increased company revenues. Implementing such a strategy involves specific steps, which we will now discuss.
1. Identify Behavioral Variables
Select the key metrics you need to track for behavioral market segmentation. Common variables include purchase history, website or app behavior, interactions across marketing channels, and more. Choose those that align most closely with your objectives.
2. Collect Data
Leverage the capabilities of your customer relationship management system to collect relevant behavioral data. Website analytics tools and marketing automation platforms are also valuable sources of information. Conduct surveys of your target audience to get first-hand opinions from consumers.
3. Segment Your Customers
When segmenting your customer base, input the aspects and characteristics required for your marketing activities. For example, to find active and generous customers, enter conditions for behavioral segmentation that align with this trait:
Made X purchases within 1 week/month/year (depending on the business) totaling Y amount.
By adjusting these conditions, you'll create distinct segments.
After the initial segmentation, make sure that the identified segments are clearly different from each other and have unique characteristics. The groups should be large enough to be meaningful. Name the selected segments so that the title quickly explains their value or nature.
4. Develop Marketing Strategies
Create marketing communication strategies tailored to each of the identified valuable segments. These strategies should consider various aspects, such as preferred communication channels and messages that resonate with the segment participants' needs, pains, and interests. Techniques like behavioural targeting in PPC allow you to reach these segments with relevant ads based on their online actions and interests. Then, run marketing campaigns according to your strategy.
5. Analyze Campaigns Performance
After launching a campaign, it's time to analyze its effectiveness. To measure performance, track the metrics that are important to your business. The most commonly tracked KPIs include click-through rates, conversion rates, and customer lifetime value. Compare campaign results with previous ones to understand which message worked best for a particular audience segment.
6. Test and Optimize
Test strategies and tactics to optimize campaigns for various segments. Send different messages and offers to gain insights into which ones work best. Since we at Claspo run A/B tests all the time, we want to help you do them correctly and get meaningful data to optimize your strategy. That's why our marketing team has developed a universal A/B testing template with key implementation steps.
Just receive it by email and use it for your experiments with emails, landing pages, and anything else you want. If (or rather when) you employ our pop-ups, conduct A/B testing of them and track analytics directly in Claspo.
Behavioral Segmentation Tools
To implement a marketing strategy that includes behavioral segmentation, you need several tools. Let's find out which ones.
How Claspo Can Help with Behavioral Segmentation
Any type of segmentation requires a lot of high-quality customer data. For behavioral market segmentation, the information is usually based on user actions and events. However, you can enrich it with customer surveys. And guess what: Claspo widgets can help you with this task. And not only with surveys. But first things first.
Many of our ready-to-use templates can be customized into survey forms. To do this, you'll need Radio, Checkbox, and Dropdown elements for closed questions. With Radio and Checkbox elements, users can simply click the appropriate answer option.
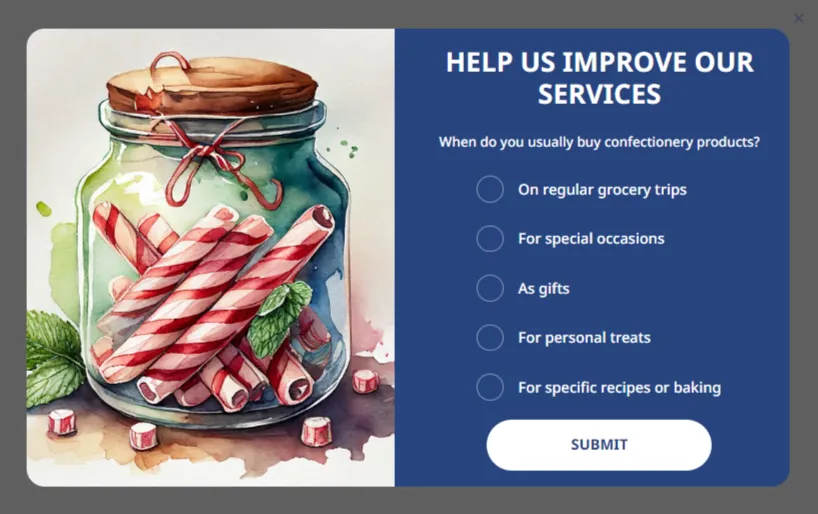
Using the Dropdown element, users select answers from a dropdown list. This option is convenient for adding several questions to a widget, fitting everything you need in a limited space.
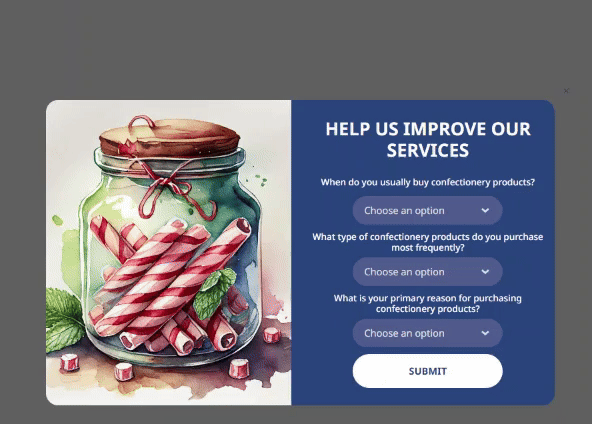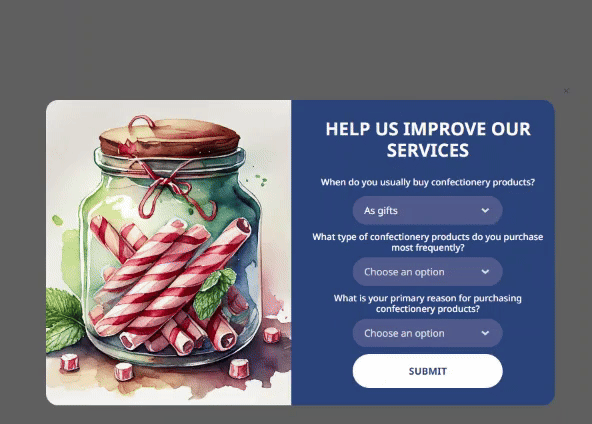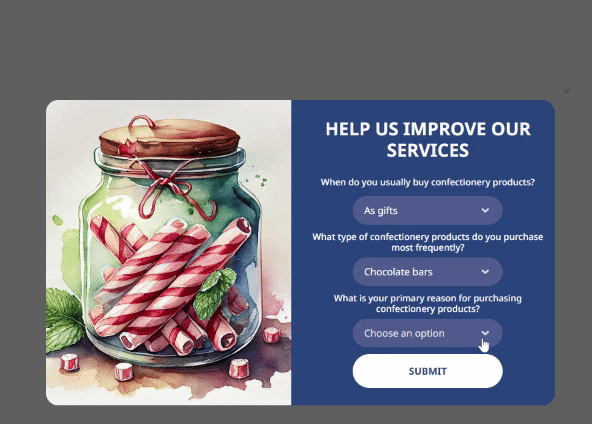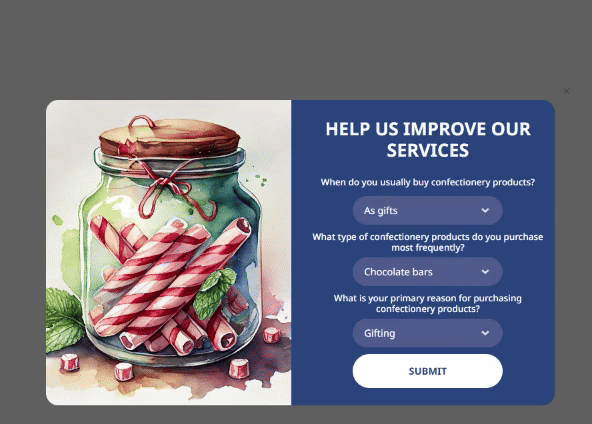
You can also add a Text field where customers can leave answers to open-ended questions. This will help you get original responses that are potentially rich in insights.
It may seem that a couple of questions are insufficient for segmentation, but this is not true. For example, answers to the question ‘When do you usually buy confectionery products?’ can help identify several consumer groups.
With behavioral targeting, we can offer relevant promotions to different segments, such as:
- Special occasions: holiday-themed promotions, gift wrapping, and seasonal products.
- Regular buyers: loyalty programs, subscription services, or personal discounts.
- Routine shoppers: promotions timed with common grocery shopping days, like before the weekend.
- Personal treaters: tempting offers with novelties and delicacies.
- Gift buyers: premium packaging options or customizable gift boxes before major holidays.
- Cooking enthusiasts: recipe ideas, bulk purchase discounts, and special ingredients.
All this segmentation can come from just one widget with a single question! Additionally, our pop-ups can help you to create personalized offers for different segments. Claspo integrates seamlessly with CRM, ESP, CDP, and more. The information collected by the widgets is automatically transferred to your platform of choice to enrich customer data. For example, you can send a promotional email to a selected segment and set up a widget with a special offer on your website that appears exclusively to visitors from this email. This way, a person sees an offer relevant to their interests and is more likely to take advantage of it.
Leveraging CMS Insights for Behavioral Segmentation
If your website is powered by a CMS, like WordPress, leverage the platform's behavioral segmentation capabilities. These systems track visitors' actions on your website:
- the pages they visit,
- how long they stay,
- whether they complete subscription forms,
- which page elements they interact with, and more.
They also provide statistics on user engagement with different content types, such as blog posts, videos, or downloadable lead magnets. By analyzing consumers' online behavior patterns, you can discern their interests, identify pages that attract valuable customers, and more. This data-driven approach enables you to generate hypotheses for improving website user experience, optimizing content, and more. If your CMS platform has very limited statistics, integrate Google Analytics and get all the necessary information. Read more about GA capabilities here.
The Role of CRM in Behavioral Segmentation
CRM systems serve as vital tools for behavioral segmentation, equipped with functionalities to track and analyze customer actions comprehensively. They gather and centralize data from various customer touchpoints, including:
- sales interactions,
- customer service inquiries,
- marketing campaigns,
- social media engagements.
These platforms enable the creation of unified customer profiles enriched with data on purchase history, website and app activity, and interactions across direct communication channels.
In addition to data collection and analysis, CRM systems provide segmentation tools to categorize customers based on behavior, such as frequent customers, regular clients, high-value buyers, engaged email subscribers, and more. Many platforms offer customizable segment creation, allowing businesses to define conditions tailored to their specific objectives.
How ESPs Drive Targeted Communication
ESPs also help organize customers into groups and, most importantly, use this information to communicate with the targeted audience. When collecting data about how people behave, these platforms are experts at tracking what subscribers do with emails, like opening them, clicking on links, sharing them, or unsubscribing.
In ESPs, you can make special groups based on the latest data about how users behave. For example, you can make a segment of subscribers who went from email to your website in the past month. You can also create custom groups based on specific conditions, like subscribers who opened a certain email and then visited a particular page on the website.
Once you've made these groups, you can send them emails with deals that match what each group is interested in. You can also set up triggered emails to be sent automatically, like a welcome series for new subscribers.
Integrate Claspo with your ESP to automatically transfer the data collected by widgets for further segmentation and personalized email campaigns.

How To Use ChatGPT for Behavior Segmentation Strategies
The most popular AI language model, ChatGPT, can also become a valuable tool for launching a behavioral customer segmentation strategy. Of course, the system will not divide the database into groups, but it will help you navigate many related issues. For example, the chat will guide you in how to analyze customer behavior. It will suggest hypotheses to be tested and advise you on metrics to analyze. We used the following prompt:
‘Please provide me with examples of hypotheses for analyzing customer behavior from different segments and list the data that will be required for such an analysis’.
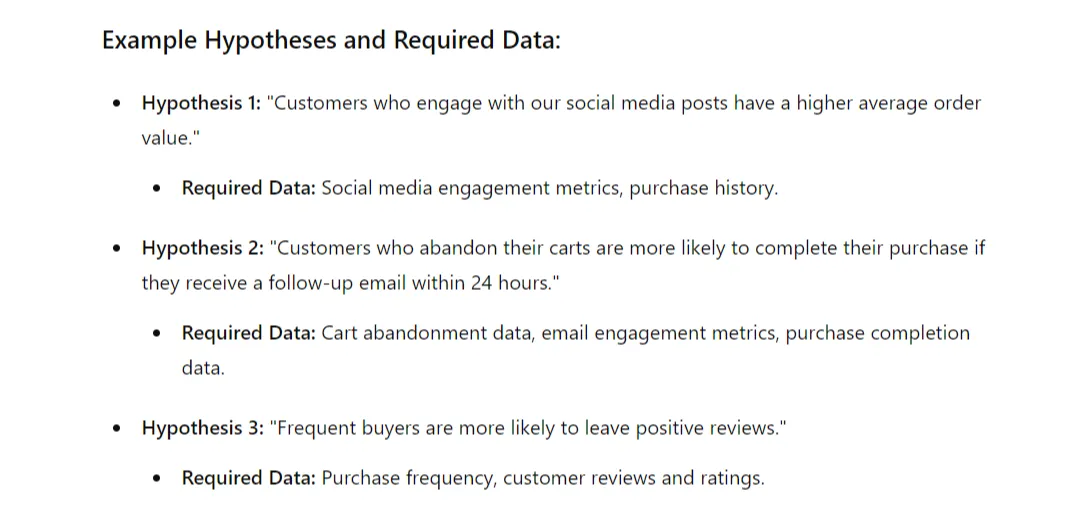
It will also help you develop strategies for personalizing marketing campaigns for specific segments. To do this, the chat will require the following data from you:
- Behavioral data (purchase history, website interactions, email engagement, etc.).
- Criteria used to segment your audience (e.g., high-value customers, frequent purchasers, new subscribers, and so on).
- Access to existing marketing materials (emails, social media content, landing pages).
- Clear objectives and goals for each marketing campaign.
- Historical campaign performance data (open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates, etc.).
For example, we wrote the following prompt in Chat GPT:
Please develop a personalized email campaign strategy for an online bakery store for the ‘high-value customers’ segment of consumers:
- men aged 35-45 years;
- average number of product pages viewed on the website over the past 3 months - 10;
- number of abandoned shopping carts in the last 3 months - 3;
- number of purchases in the last 3 months - 8;
- Email Open Rate - 55%;
- Click Rate - 20%.
Objective: Maximize revenue from the high-value customer segment.
- Goal 1: Increase average order value by 20% among the segment within the next quarter.
- Goal 2: Encourage at least 30% of high-value customers to make repeat purchases within the next six months.
- Goal 3: Improve customer satisfaction and loyalty scores among high-value segments by 10% through personalized experiences and rewards.

In response, we received a comprehensive strategy consisting of six steps. It outlined actions for each month of the first quarter. Additionally, there was an emphasis on analyzing mailing performance and implementing improvements from the fourth to the sixth month.
The chat will also assist you in formulating survey questions and analyzing the feedback received. This article explains this more.
It’s Time to Behave!
Behavioral segmentation helps businesses effectively tailor their marketing strategies and communications to the needs and preferences of a diverse client base. By analyzing information about customer behavior, such as purchase frequency, loyalty, and engagement levels, companies can create personalized experiences that drive customer satisfaction and loyalty and, ultimately, revenue growth. Examples from leading brands such as Sephora and Starbucks illustrate the power of behavioral segmentation in action.
Implementing the segmentation strategy involves collecting relevant data, grouping customers, and continuously testing and optimizing marketing efforts. Tools such as Claspo can make this process easier by providing the necessary infrastructure for efficient data collection and targeted communication.
So, if you're not with us yet, it's time to get on board! Moreover, you can use all the functionality and templates with our Lifetime Free Plan. See for yourself the power of Claspo widgets and convert more customers quickly!
Behavioral Segmentation FAQs
1. What are the benefits of using behavioral segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation allows marketers to understand their target audience better and create more personalized campaigns, resulting in improved customer engagement and increased sales. It also helps marketers identify customer trends and develop more effective acquisition and retention strategies.
2. How is behavioral segmentation different from demographic segmentation?
Demographic segmentation is based on demographic factors such as age, gender, location, and income. Behavioral segmentation is based on individual customer behavior and preferences. While demographic segmentation provides a broad, generalized view of the customer base, behavioral segmentation provides a more detailed and nuanced understanding of customer needs and preferences.
3. What are marketing channels involved in behavioral segmentation?
Behavioral segmentation uses all channels to the maximum: email marketing (reactivation, trigger emails, abandoned carts, surveys, and so on), social media, instant messengers, and others.







The topic of the three primary factors that impact consumer behavior is fascinating. I am eager to learn more about how marketers can effectively influence these factors when targeting their audience.
About five years into my marketing career, I was part of a project that employed strategies similar to the ones this piece elaborates on. By zeroing in on our customers' behaviors and adjusting our communication strategies accordingly, we observed a substantial surge in user engagement and conversions. This experience reiterated the potency of personalized customer-centric tactics, which remain key to successful marketing outcomes.